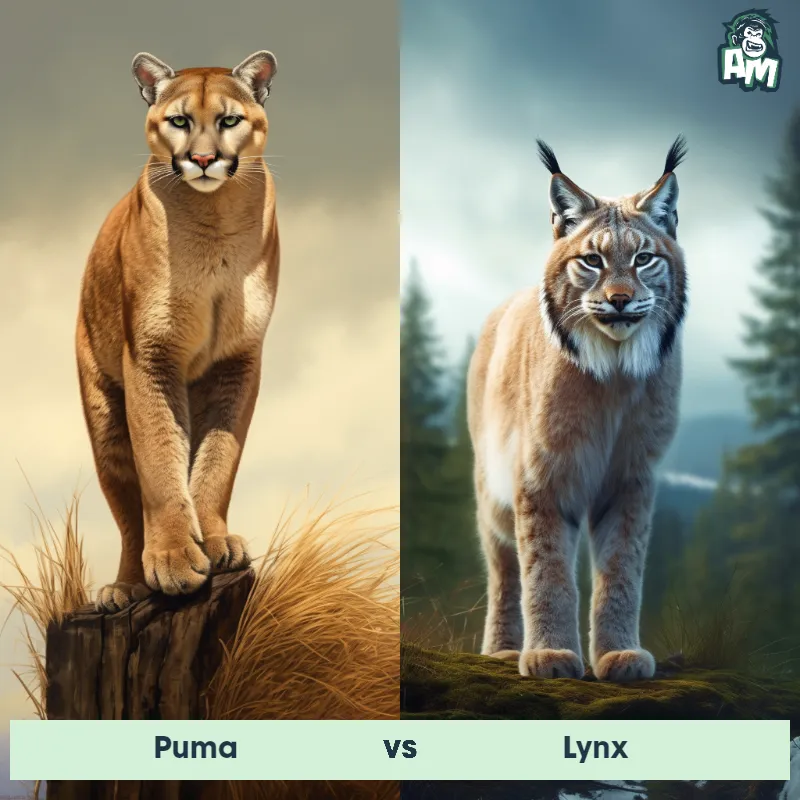
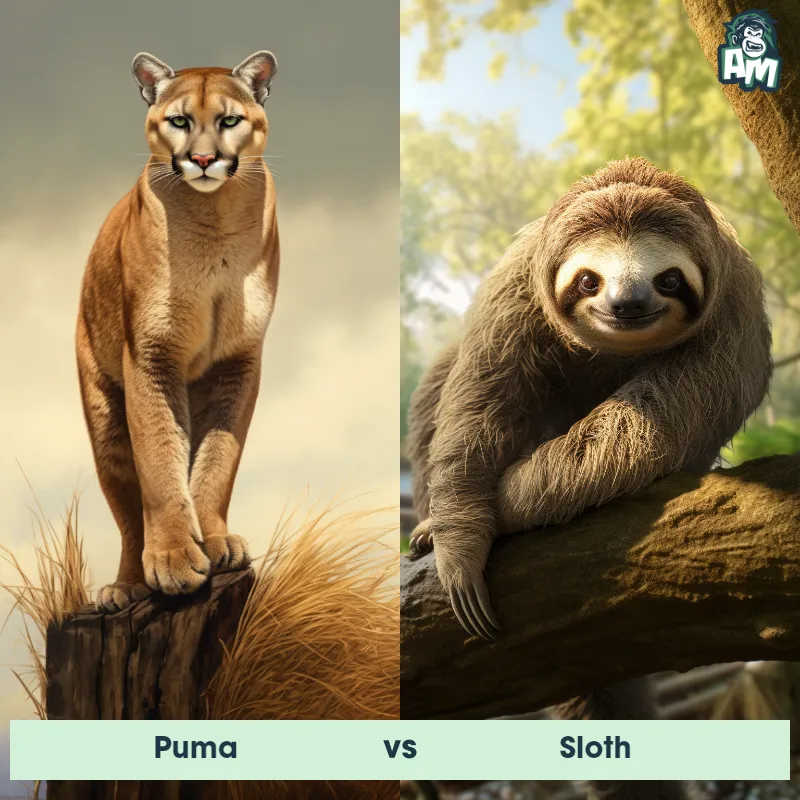
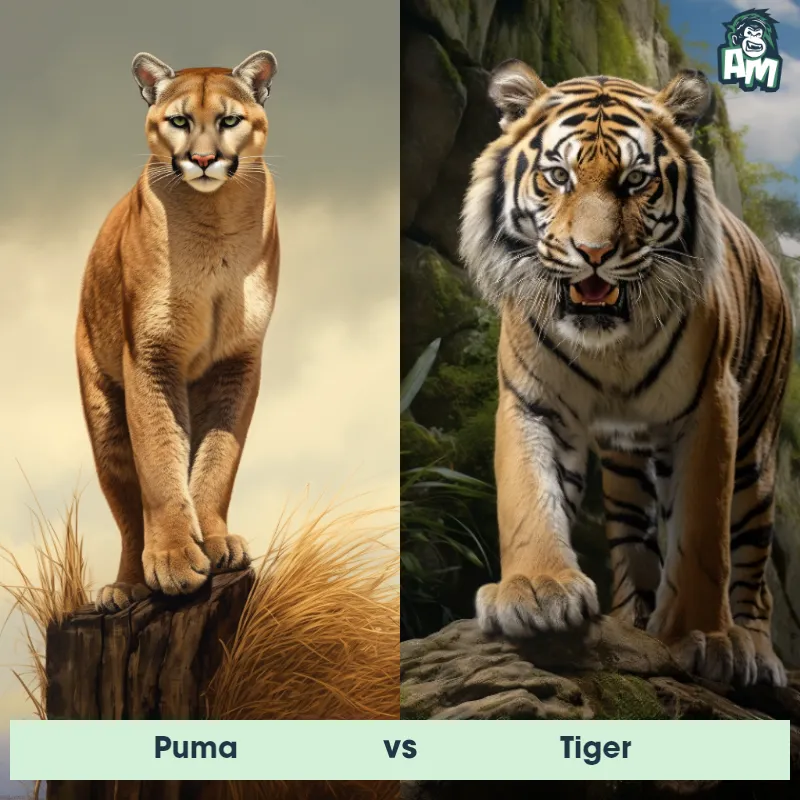
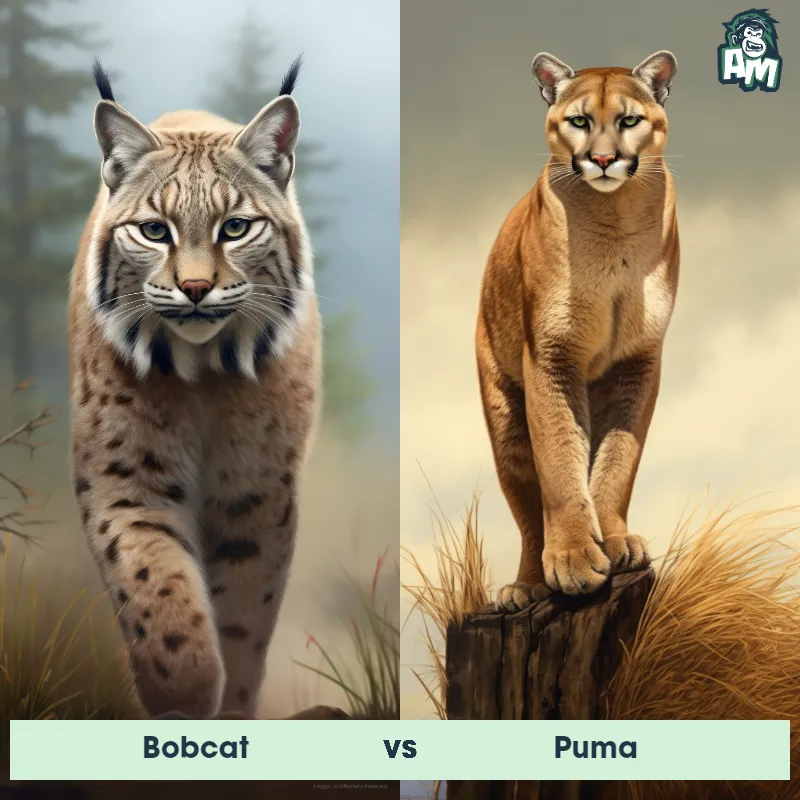
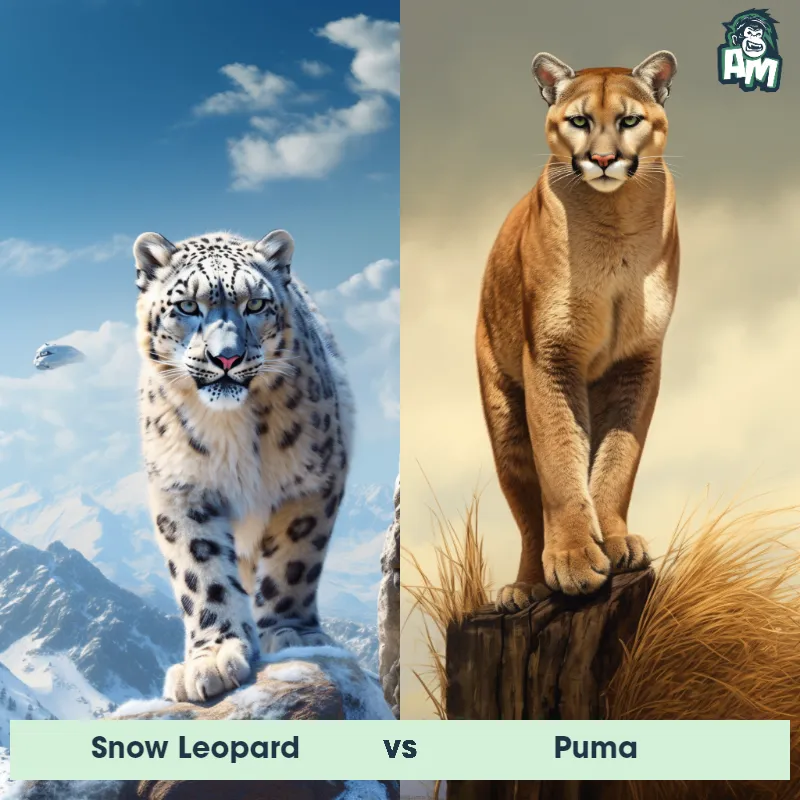
The Puma
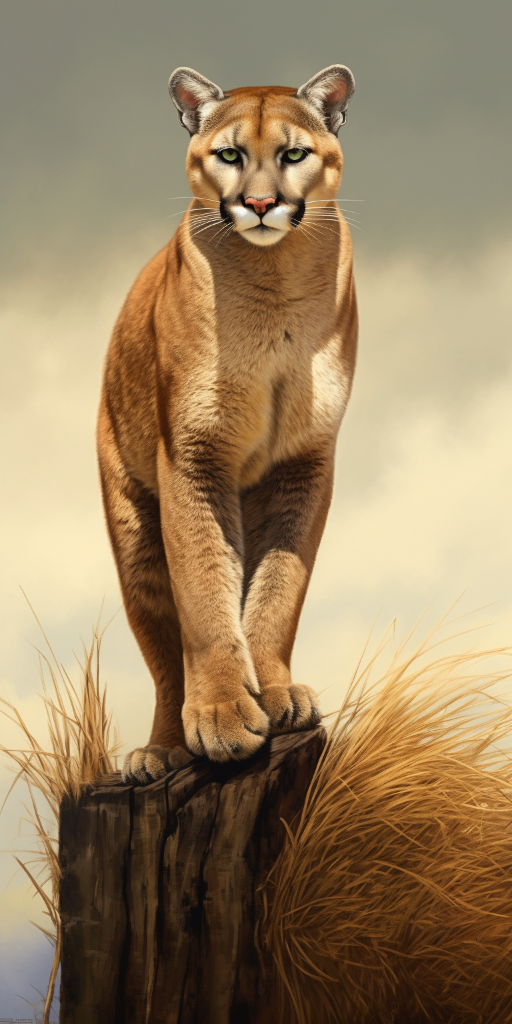
The Puma, also known as the cougar or mountain lion, is a large wild cat that is native to the Americas. They are known for their agile and stealthy nature, making them excellent hunters. Pumas have a compact and muscular body, with a tan or reddish-brown coat and a long tail. They have strong legs with retractable claws, enabling them to climb trees and pounce on their prey with precision. Pumas are solitary animals, marking their territory with scent and vocalizations. They are known for their adaptability, being able to live in a variety of habitats including forests, mountains, and deserts.

| Puma | |
|---|---|
| Size | 2-3 feet (0.6-0.9 meters) at the shoulder |
| Weight | 100-200 pounds (45-90 kilograms) |
| Speed | Speed: 50 mph (80.47 km/hr) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaws and sharp claws |
| Biggest Weakness | Vulnerable to attacks from behind |
| Scientific Name | Puma concolor |
| Family | Felidae |
| Habitat | Mountains, forests, deserts |
| Geography | North and South America |
| Diet | Carnivorous, primarily deer and smaller mammals |
| Lifespan | 8 years - 13 years |

The Puma
The Puma, also known as the cougar or mountain lion, is a large wild cat that is native to the Americas. They are known for their agile and stealthy nature, making them excellent hunters. Pumas have a compact and muscular body, with a tan or reddish-brown coat and a long tail. They have strong legs with retractable claws, enabling them to climb trees and pounce on their prey with precision. Pumas are solitary animals, marking their territory with scent and vocalizations. They are known for their adaptability, being able to live in a variety of habitats including forests, mountains, and deserts.
Fun Fact: The Puma is one of the most powerful predators in the animal kingdom, capable of taking down prey much larger than itself, such as deer and elk.
| Puma | |
|---|---|
| Size | 2-3 feet (0.6-0.9 meters) at the shoulder |
| Weight | 100-200 pounds (45-90 kilograms) |
| Speed | Speed: 50 mph (80.47 km/hr) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaws and sharp claws |
| Biggest Weakness | Vulnerable to attacks from behind |
| Scientific Name | Puma concolor |
| Family | Felidae |
| Habitat | Mountains, forests, deserts |
| Geography | North and South America |
| Diet | Carnivorous, primarily deer and smaller mammals |
| Lifespan | 8 years - 13 years |
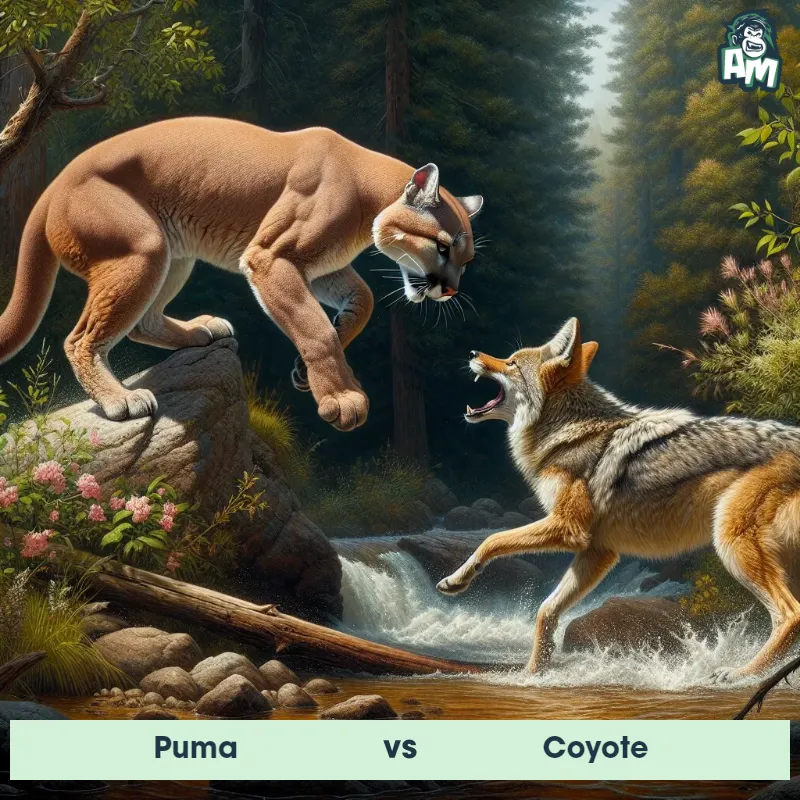
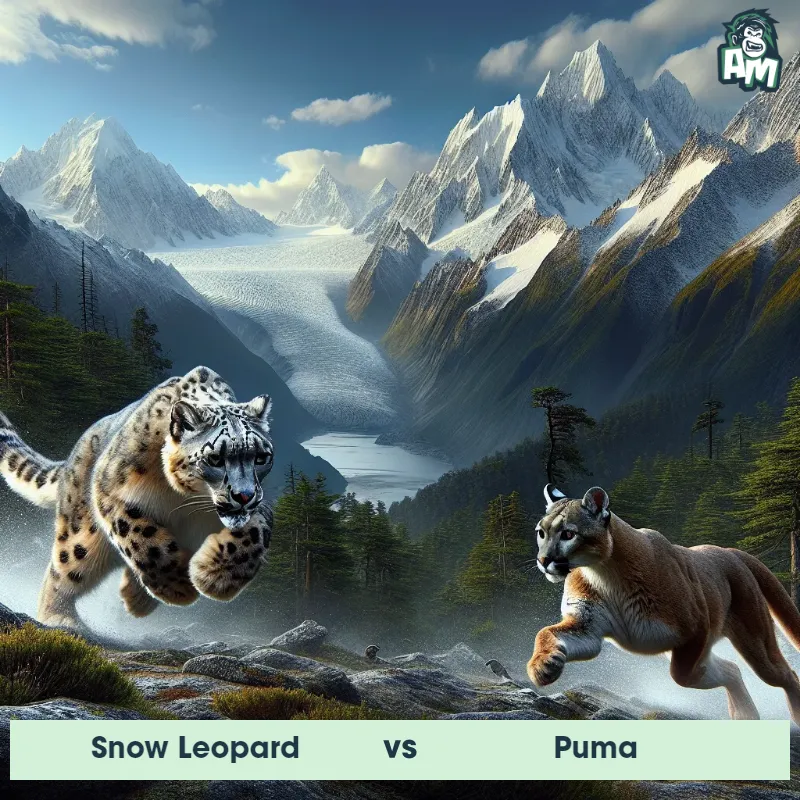
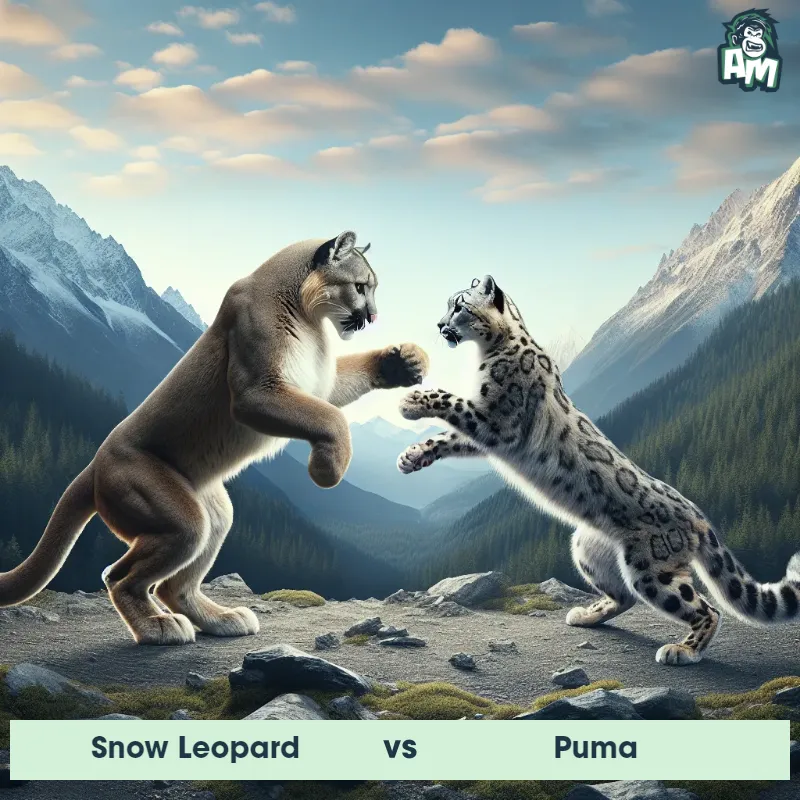
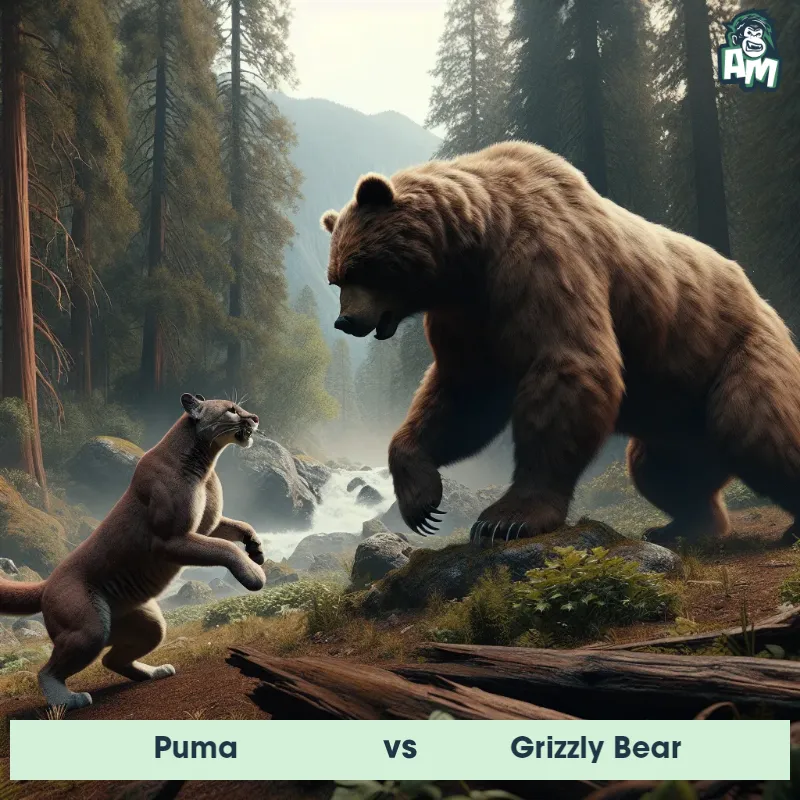
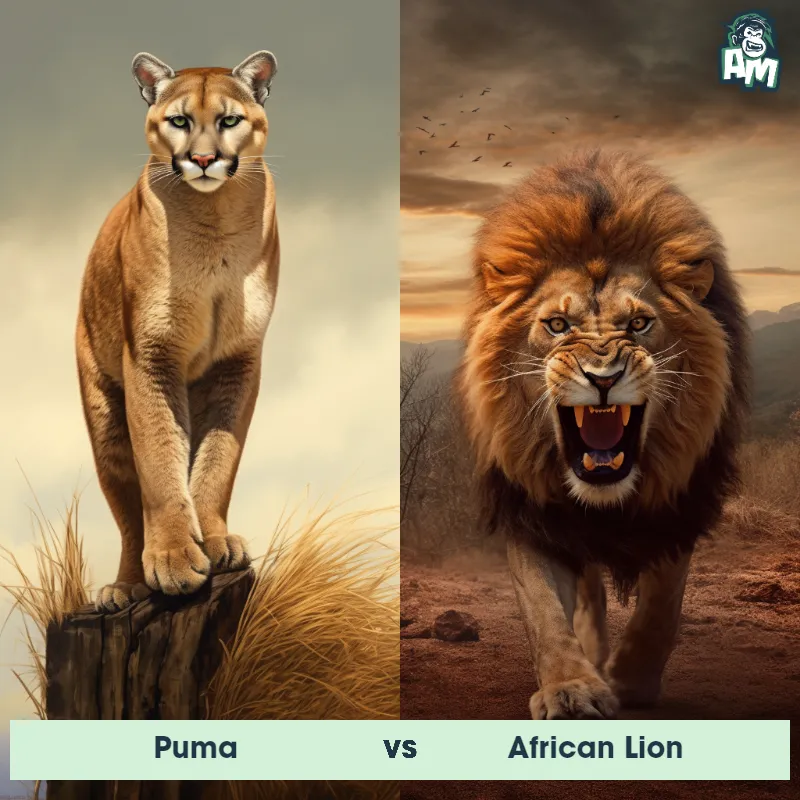
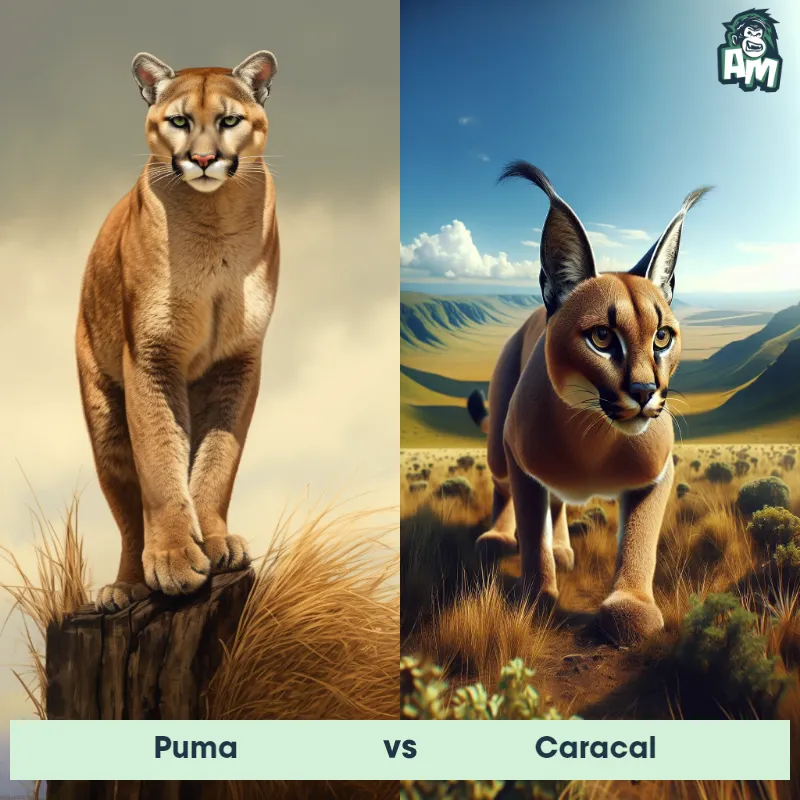
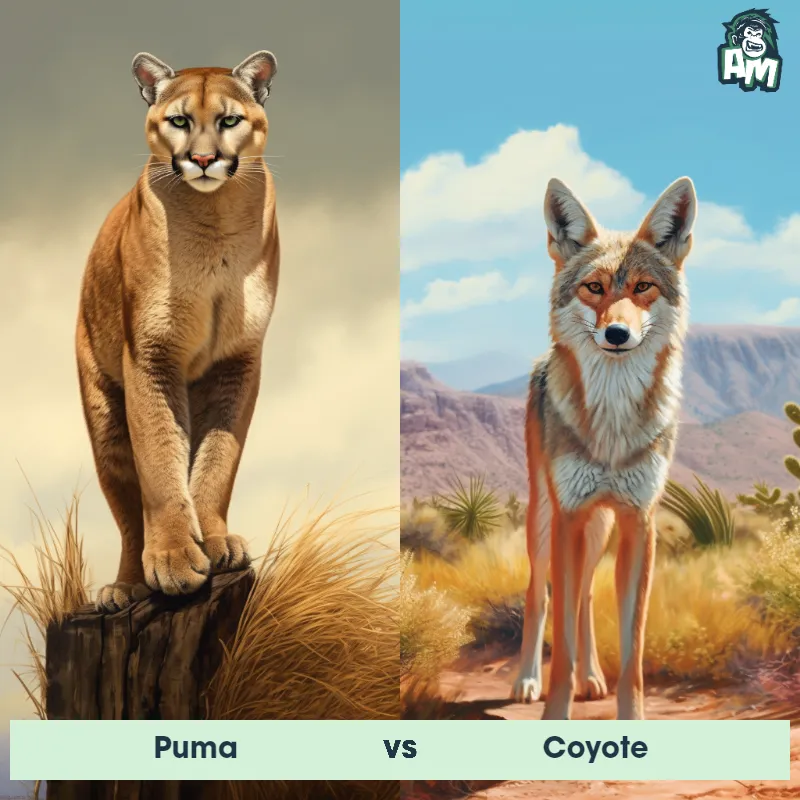
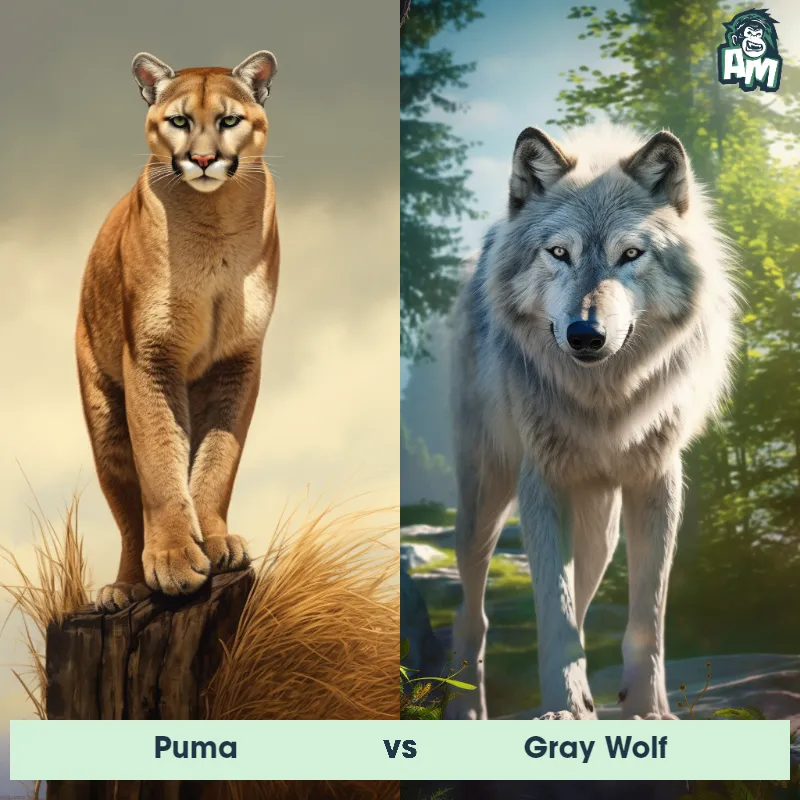
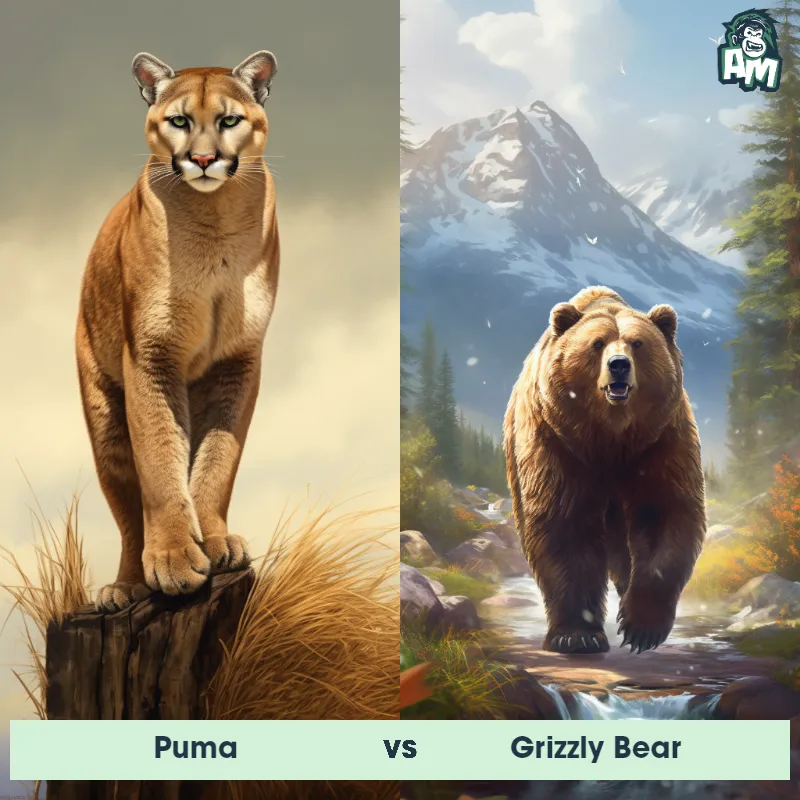
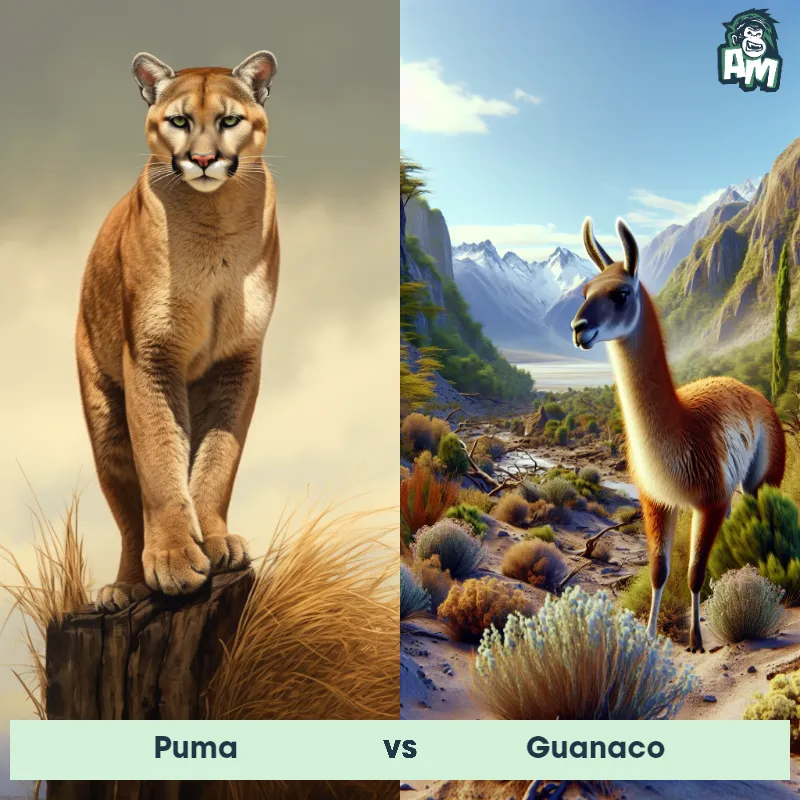
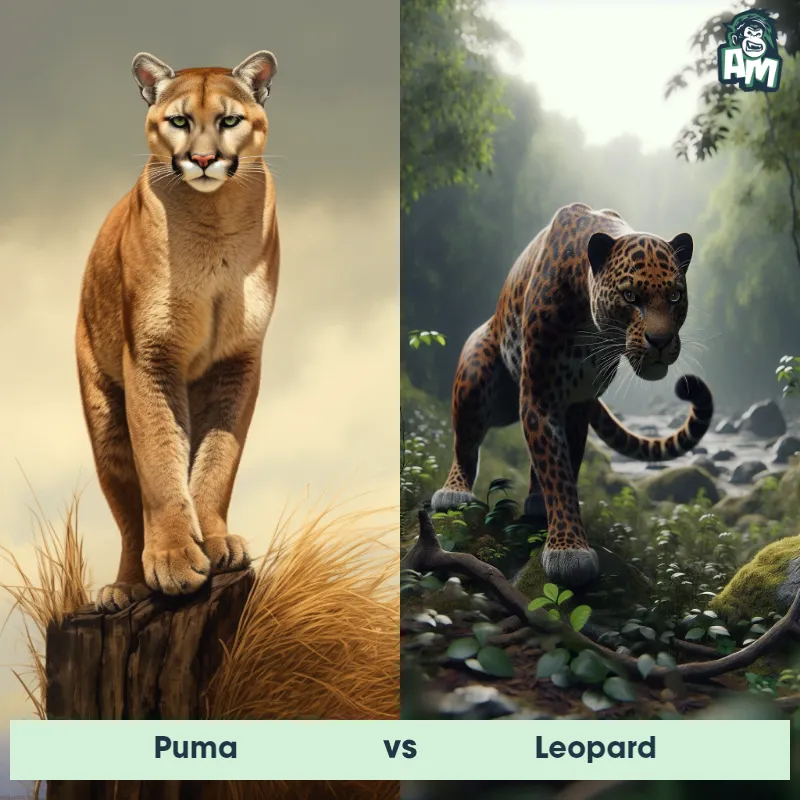
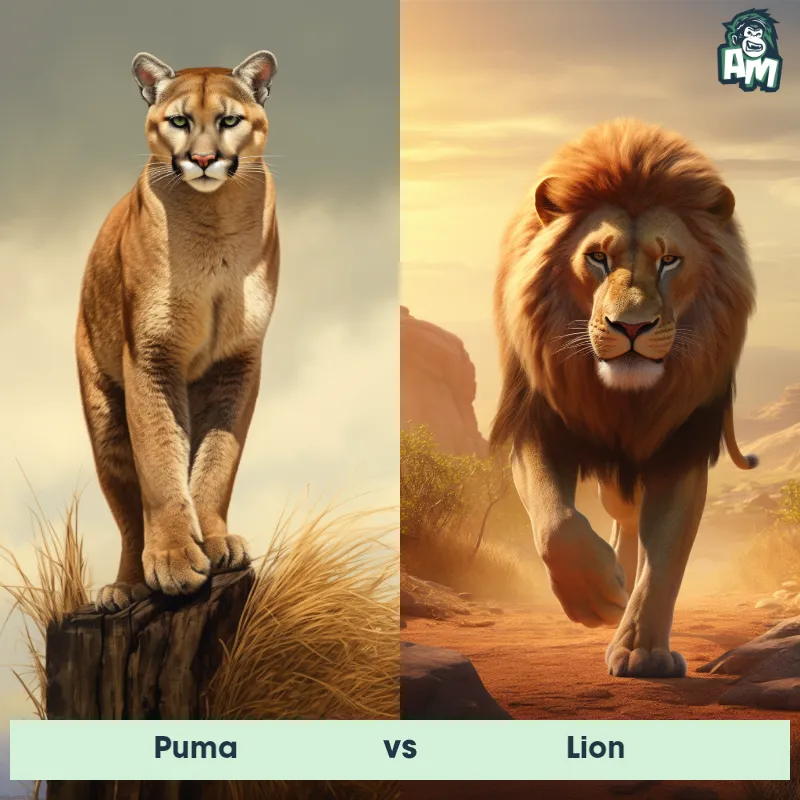
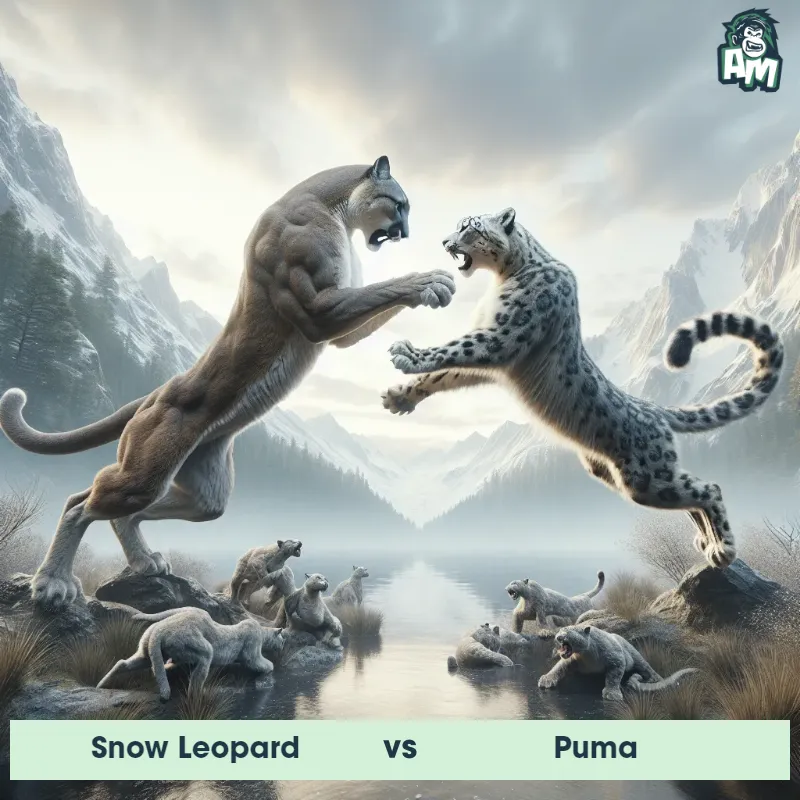
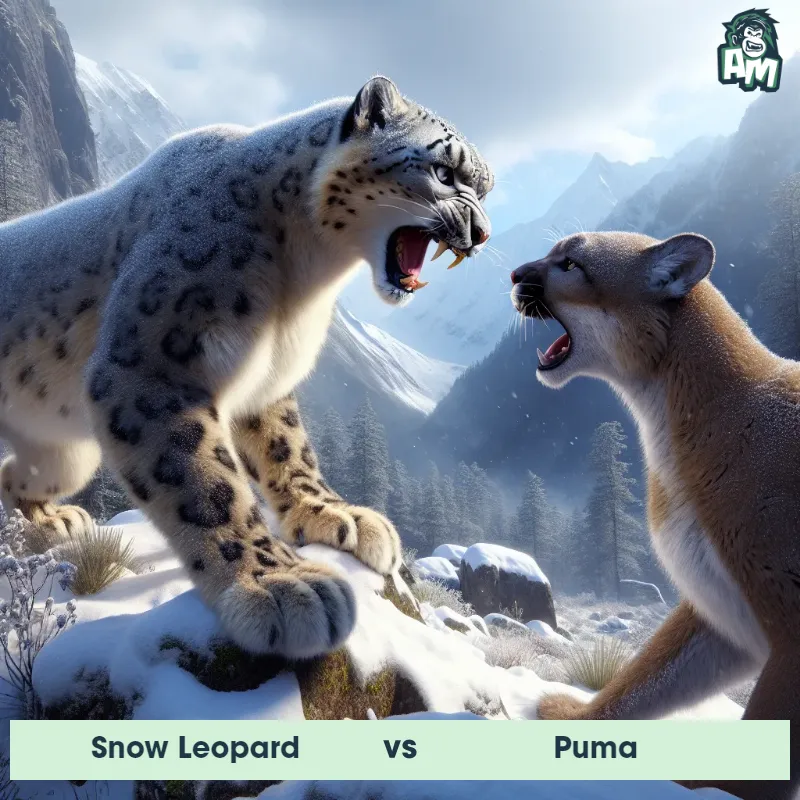
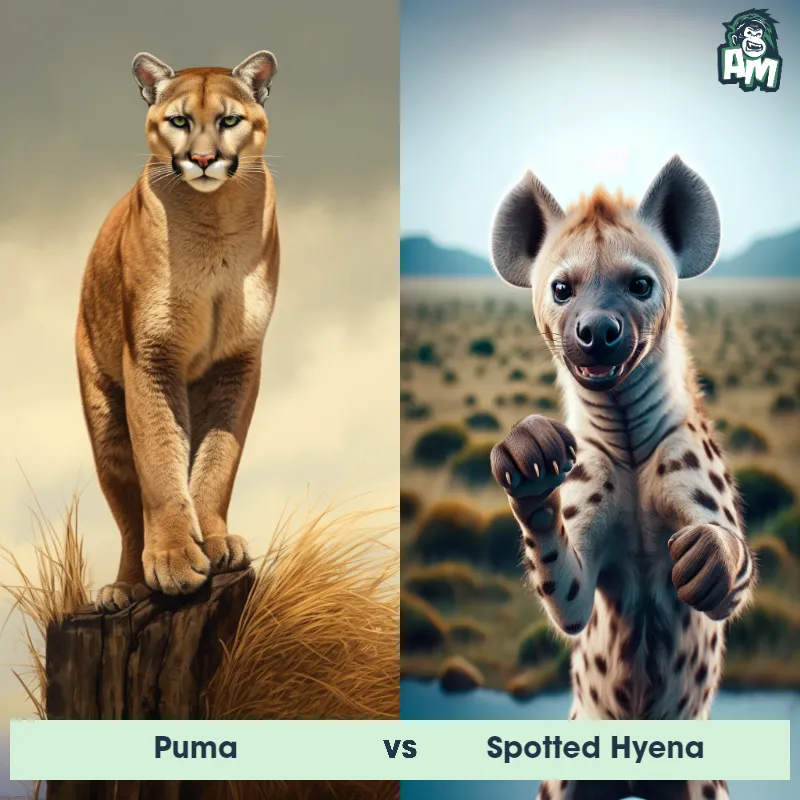
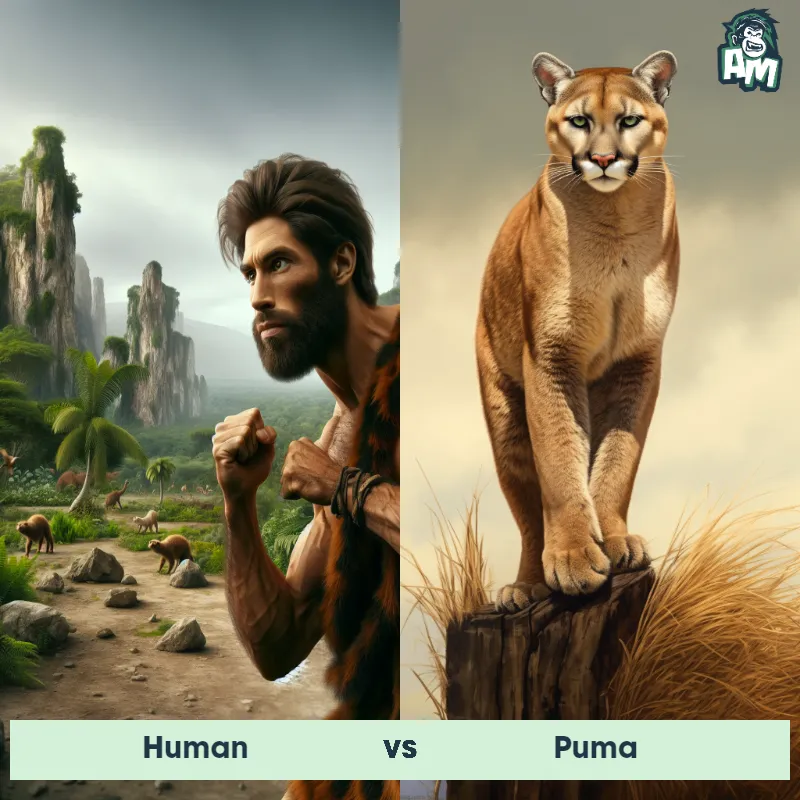
Match Highlights
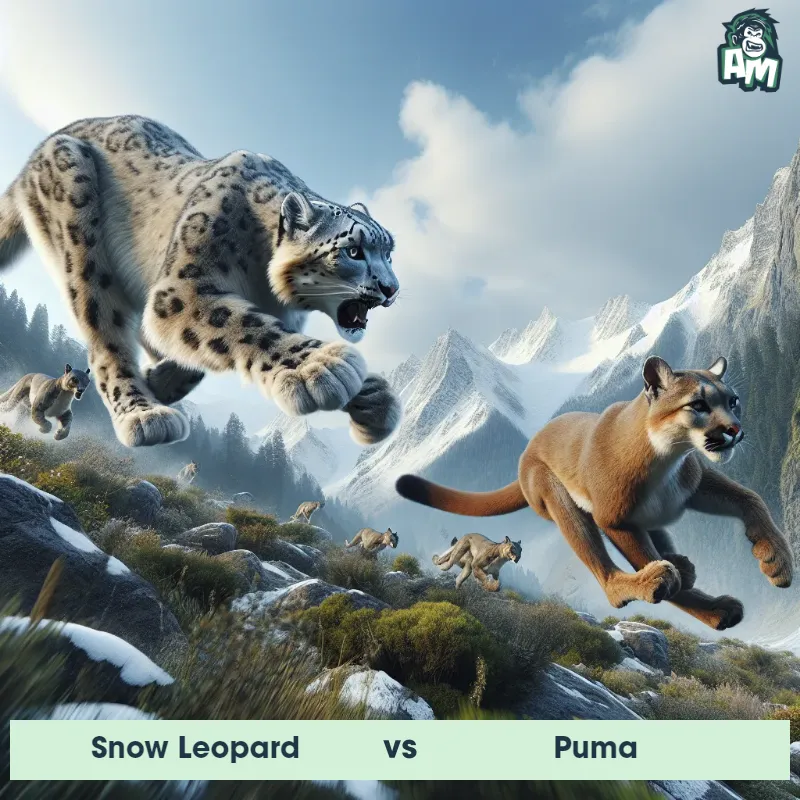
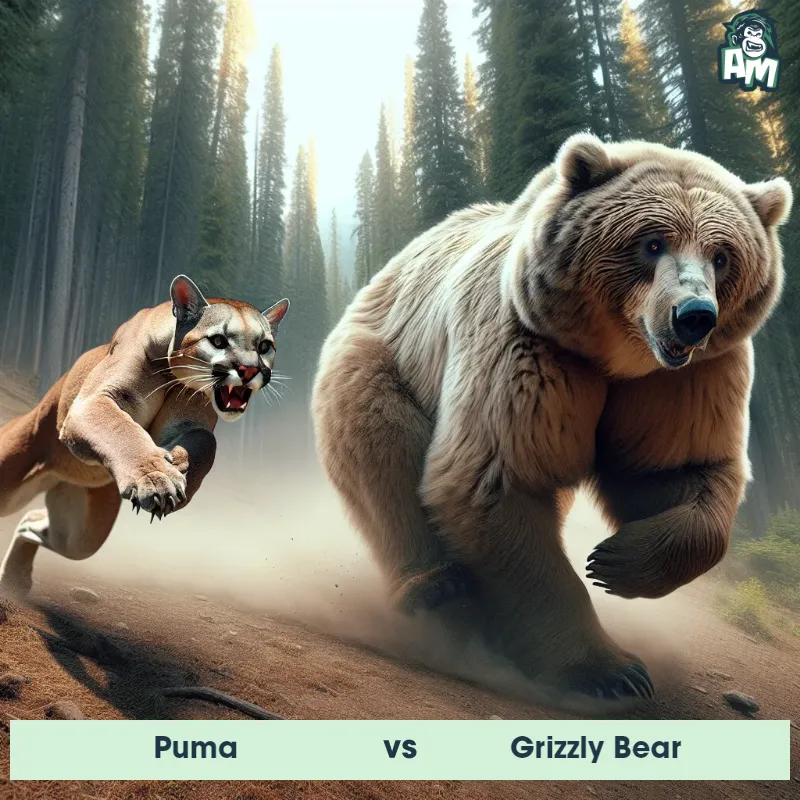
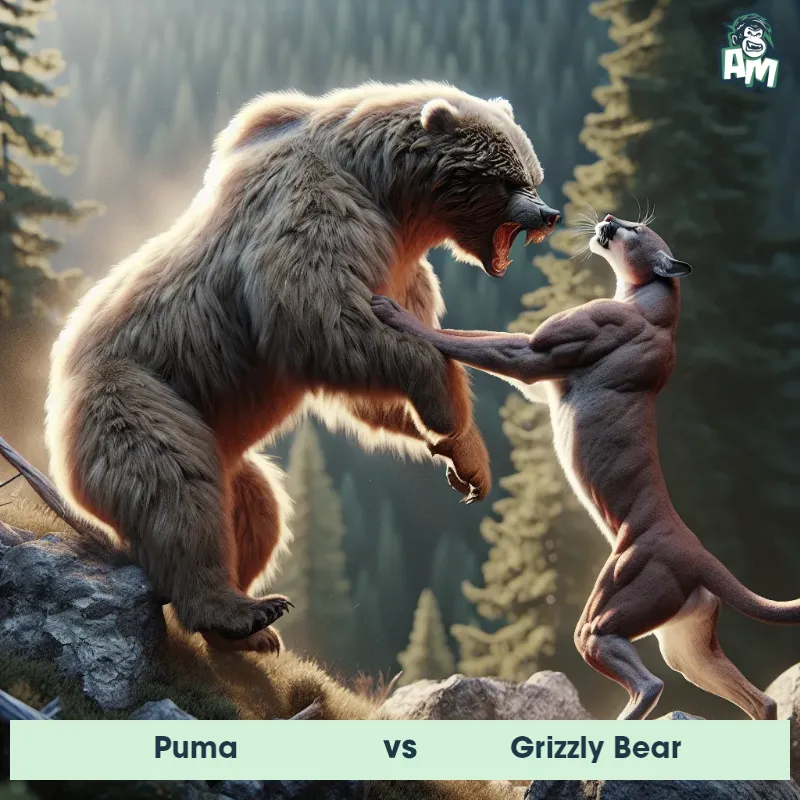
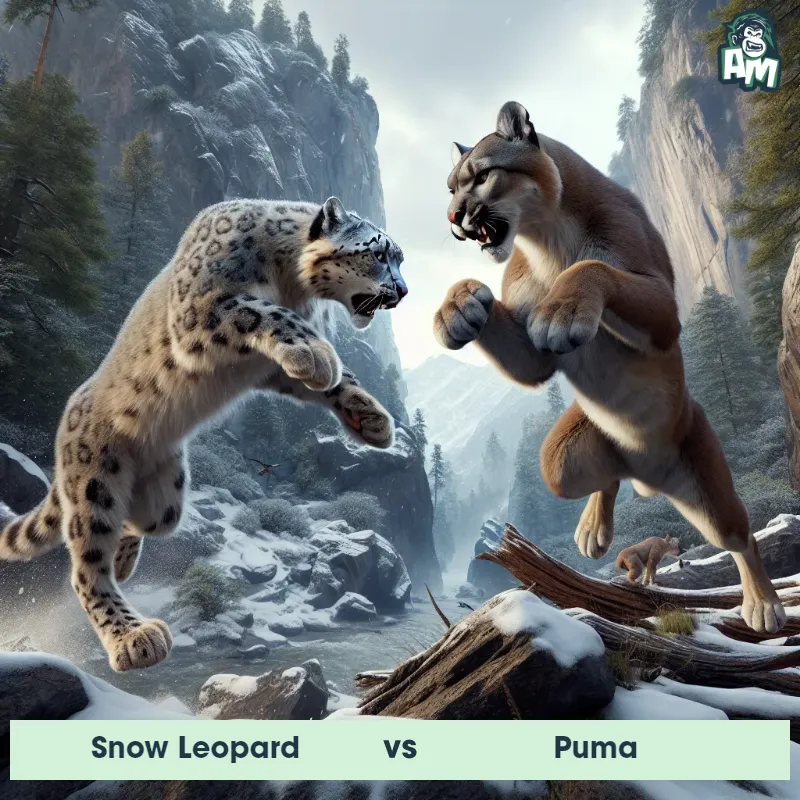
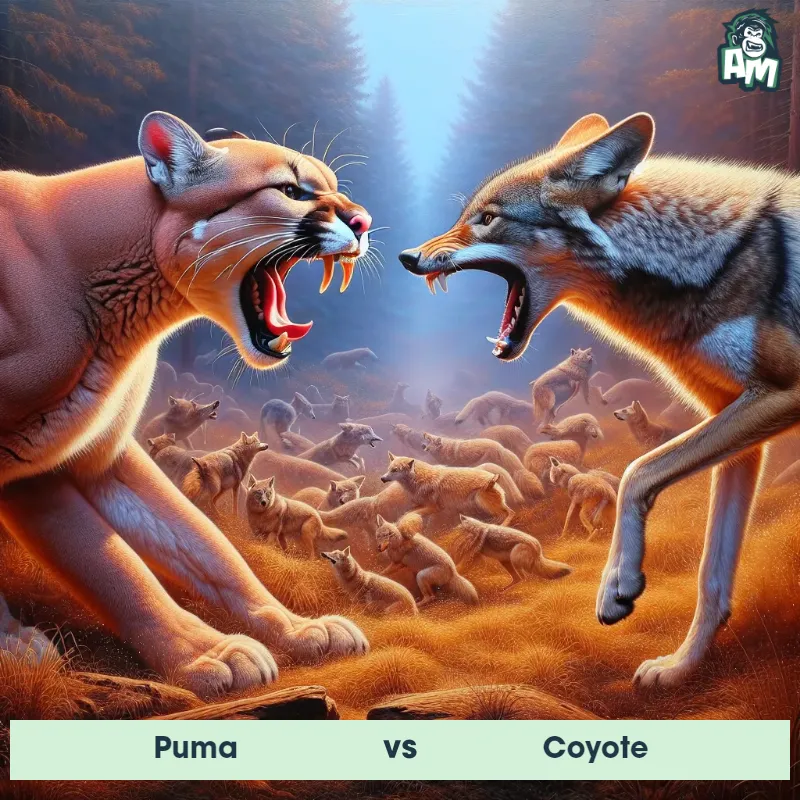
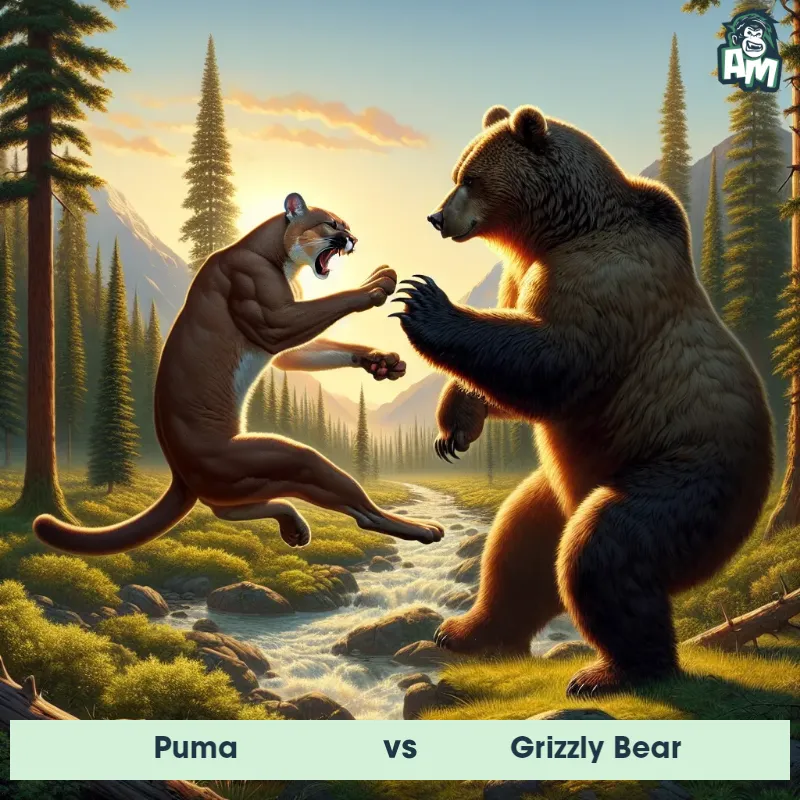
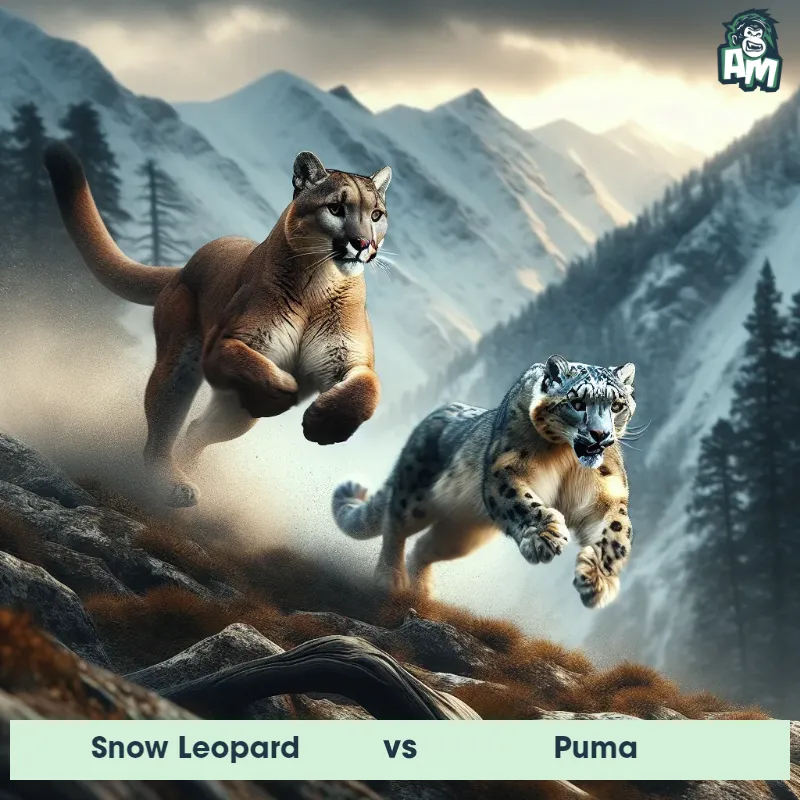
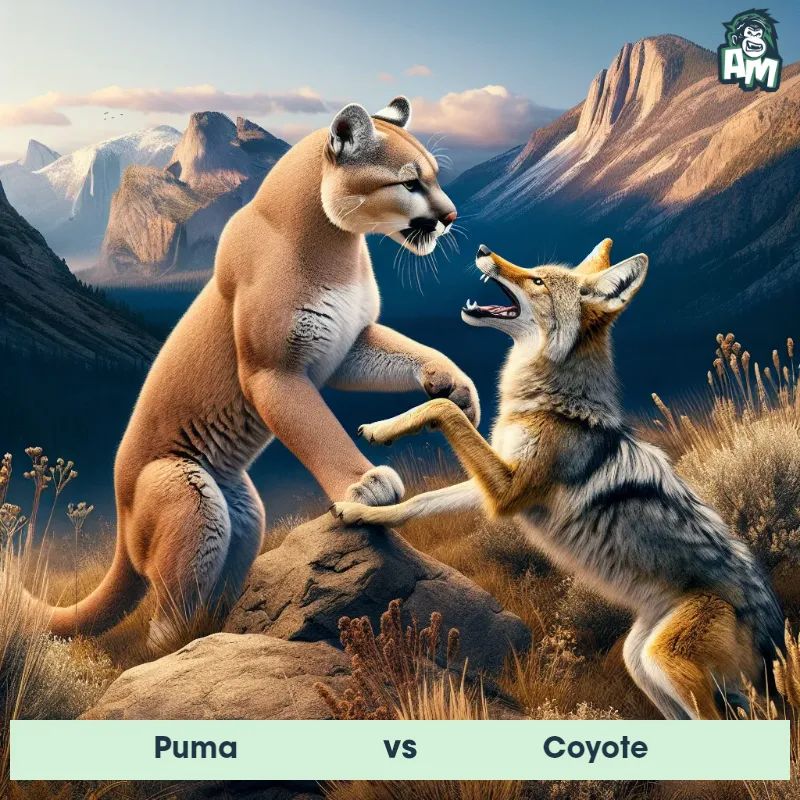
Puma Matchups
We use AI to simulate matchups between the Puma and other animals. Our simulation considers size, strength, and natural predatory behaviors to determine the most likely outcome.
Puma: Diet, Predators, Aggression, and Defensive Behaviors
What do Pumas eat?
Pumas, also known as mountain lions or cougars, are carnivorous animals that mainly feed on deer, elk, and other large mammals. They are opportunistic hunters and will also consume smaller prey such as rabbits and rodents. Pumas are solitary predators that rely on stealth and strength to ambush and overpower their prey.
Do Pumas have any predators?
Pumas are apex predators and do not have any natural predators in their ecosystem. However, young or injured pumas may fall prey to other large carnivores such as bears or other pumas. Human activities, such as hunting and habitat destruction, are the main threats to puma populations.
Are Pumas aggressive?
Pumas are generally solitary and elusive animals that avoid confrontation with humans. However, they may become aggressive if they feel threatened or cornered. Pumas are known to defend their territory and young with displays of aggression, such as growling, hissing, or swatting with their paws.
Do Pumas fight?
Pumas are solitary animals that typically avoid conflict with other pumas except during the breeding season or when establishing territories. During such interactions, pumas may engage in fights to establish dominance or defend their territory. These fights can be intense and may result in injuries to the combatants.
How do Pumas defend themselves?
Pumas rely on their agility, strength, and stealth to defend themselves against potential threats. When feeling threatened, pumas will typically try to intimidate their aggressor through vocalizations and body language before resorting to physical confrontation. If needed, pumas will use their sharp claws and powerful jaws to defend themselves.
What is Pumas' biggest weakness in a fight?
Despite being powerful predators, pumas have certain vulnerabilities in a fight. One of their biggest weaknesses is their lack of endurance compared to their prey. Pumas are ambush predators that rely on short bursts of speed and agility to catch their prey. During prolonged fights or chases, their stamina may be a limiting factor, making them vulnerable to exhaustion.
Fun Fact: Unlike other big cats, Pumas are capable of purring, but they cannot roar like lions or tigers. Instead, they communicate through various vocalizations, including hisses, growls, and screams.
Fun Fact: Pumas have the highest jump of any cat, being able to leap up to 20 feet vertically from a standing position, allowing them to easily scale cliffs and trees in pursuit of prey.