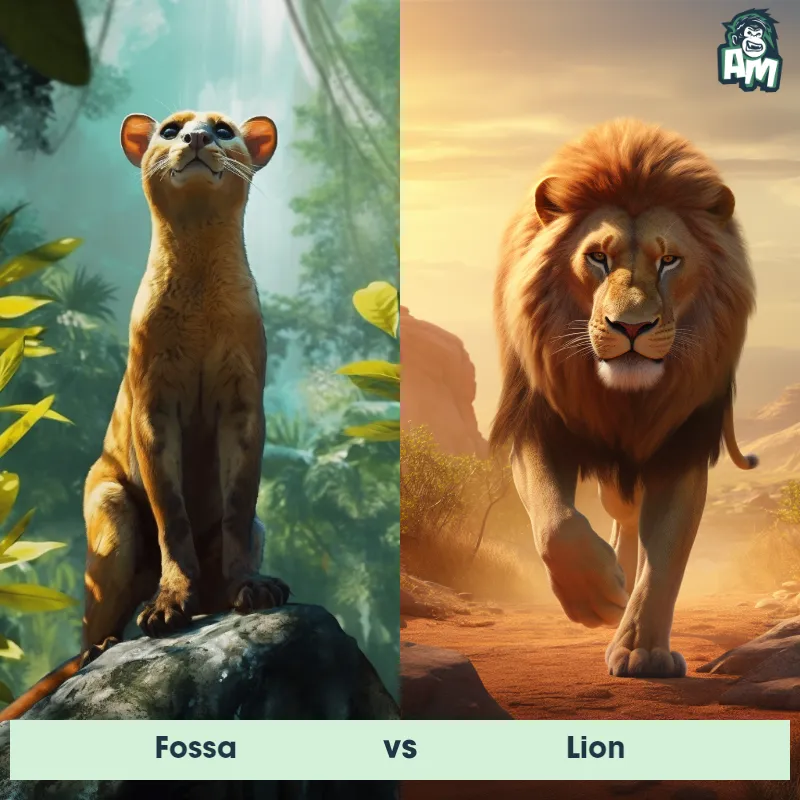
Fossa vs LemurSee Who Wins
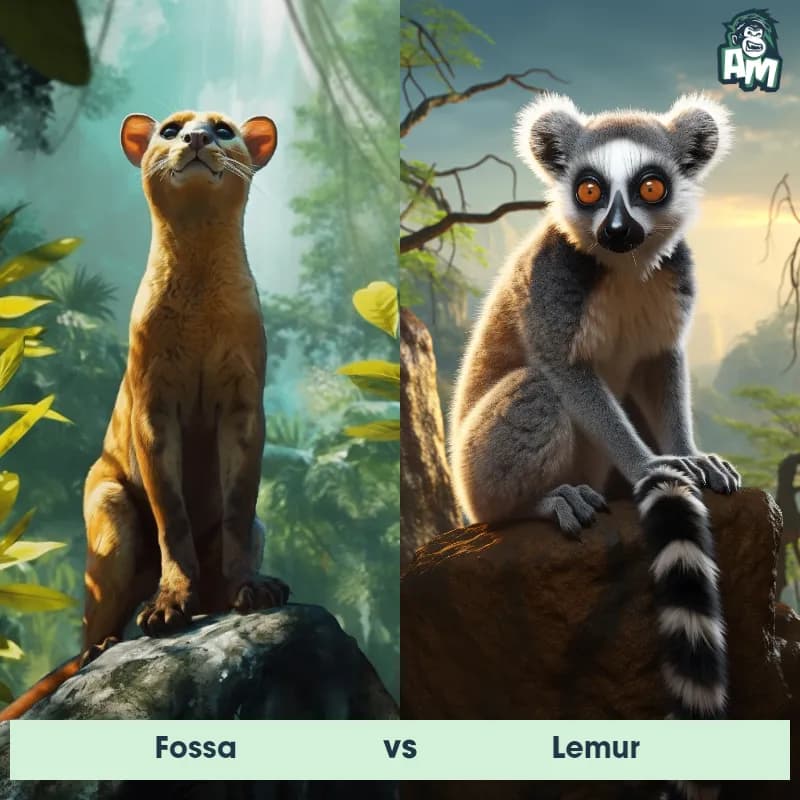

Good evening, ladies and gentlemen, and welcome to tonight's thrilling edition of animal matchup! We have an exhilarating fight lined up for you tonight between two fierce opponents. In the blue corner, we have the agile and cunning Fossa. And in the red corner, we have the nimble and energetic Lemur. Both of these creatures possess unique strengths, and this is bound to be a match for the ages. Let's dive straight into the action!
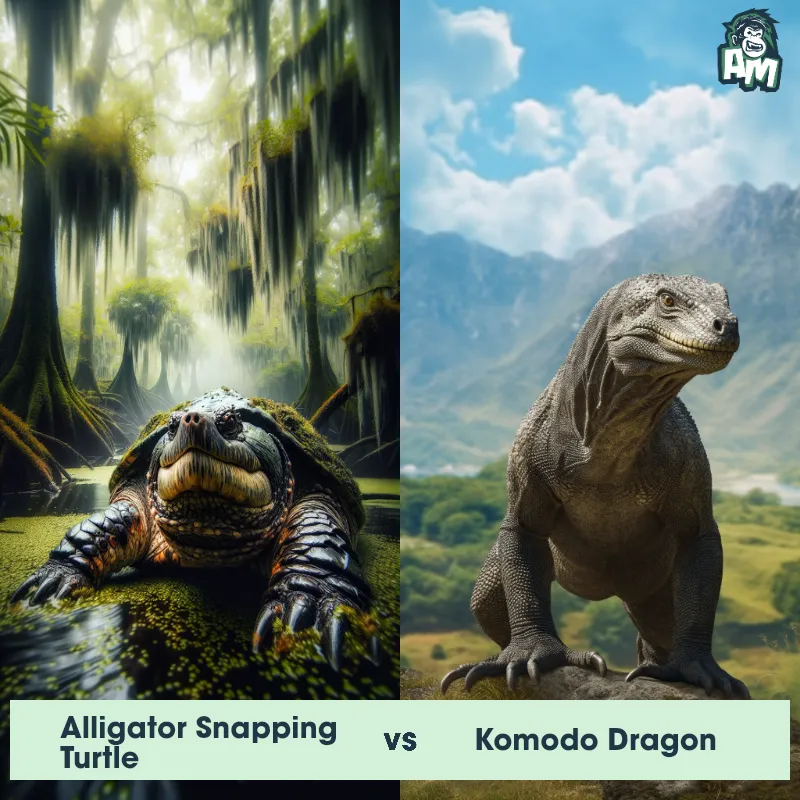
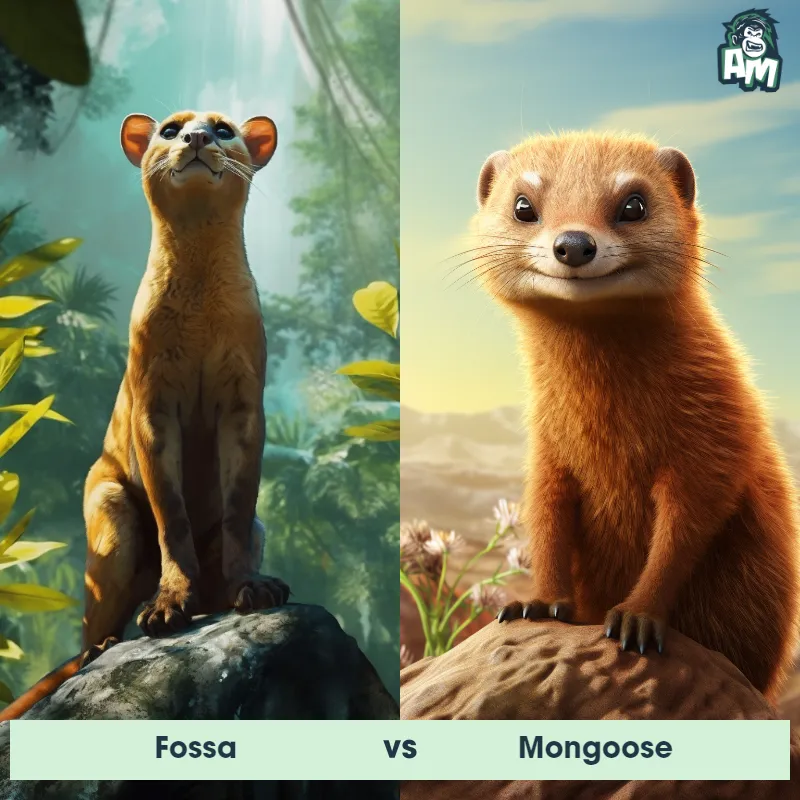
Contender 1: Fossa
The Fossa, also known as the Malagasy Civet, is a carnivorous mammal native to Madagascar. It has a slender body, short legs, and a long tail, which it uses for balance while climbing trees. The Fossa has sharp claws and teeth, making it an efficient hunter of lemurs and other small animals. It has a reddish-brown coat with a white underbelly and can grow up to 6 feet in length.
Fun Fact: The Fossa is the largest predator on Madagascar and is known for its ability to climb trees with ease, making it a formidable hunter of lemurs.
Contender 2: Lemur
The Lemur is a type of primate known as a prosimian, native to the island of Madagascar. Lemurs come in various sizes and colors, but they are typically characterized by a pointed snout, large eyes, and a long tail that can be longer than their body. Many lemur species have a thick and woolly fur that ranges in color from reddish-brown to gray and black. Lemurs are arboreal animals, spending most of their time in trees, and their diet consists of fruits, leaves, flowers, and insects.
Fun Fact: Lemurs communicate with each other using a variety of vocalizations, body postures, and scent markings, exhibiting a complex and intriguing social structure.
Matchup Stats
| Fossa | Lemur | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Up to 6 feet (1.8 meters) | 15–18 inches (39–46 cm) long (body length), 9–10 inches (23–26 cm) tall at shoulder |
| Weight | Up to 26 pounds (12 kilograms) | 2.2–3.0 kilograms (4.9–6.6 pounds) |
| Speed | Speed: 20 mph (32.19 km/hr) | 20mph (32km/h) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaws and sharp claws | Agility and speed |
| Biggest Weakness | Short legs and relatively small size | Small size and lack of aggressive behavior |
Current Votes
Fossa vs Lemur
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Fossa | Lemur | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cryptoprocta ferox | Lemuriformes |
| Family | Eupleridae | Lemuridae |
| Habitat | Forests | Forests and jungles |
| Geography | Madagascar | Madagascar |
| Diet | Carnivorous, primarily lemurs | Fruits, leaves, flowers, and insects |
| Lifespan | 15 years - 20 years | 16 years - 25 years |
Key Differences between Fossa and Lemur
- Coloration: The Fossa possesses a primarily reddish-brown coat with some variations, whereas lemurs display a diverse range of colors including grey, brown, black, and even striking patterns with vibrant hues such as white, orange, or red on their bodies.
- Ear Shape: Fossas possess relatively large, rounded ears that are located on the sides of their heads, while lemurs often have more pointed and erect ears that may even feature tufts of fur at their tips.
- Body Structure: The Fossa has a slender and elongated body with short legs and a long tail, allowing for better agility when climbing trees and moving through the forest floor. In contrast, lemurs often have more compact and round bodies, with longer limbs and tails to aid in balance while leaping between branches.
- Eye and Nose Proportions: The Fossa has relatively closer-set eyes and a relatively longer nose compared to lemurs, whose eyes are often more spaced apart and have a shorter snout in relation to their face.
- Size: The Fossa is significantly larger than most lemurs, with an average length of 70-80 cm and a weight of 5-8 kg, while lemurs can vary in size with species ranging from as small as 30 cm to as large as 70 cm and weighing between 0.5 to 20 kg.
- Facial Features: Fossas exhibit a more pointed snout with sharper and relatively larger canine teeth, giving them a more carnivorous appearance. In contrast, lemurs typically have rounder faces with a shorter snout, smaller canines, and a more herbivorous dental structure.